According to the ITU Emissions Classification, and regarding the type of intrusions received in this mode in our HF amateur bands, we can distinguish two types of signals:
CW — A1A
The ITU classification of emissions code A1A indicates:
A : Double side band.
1 : A single channel containing quantized or digital information, without the use of a subcarrier to modulate it.
A : Telegraphy for auditory reception.
They are signals transmitted in Morse code. Two examples proposed: the transmissions of the “RCV” station, and the transmissions sent by radio-location devices installed in fishing buoys
“RCV” station
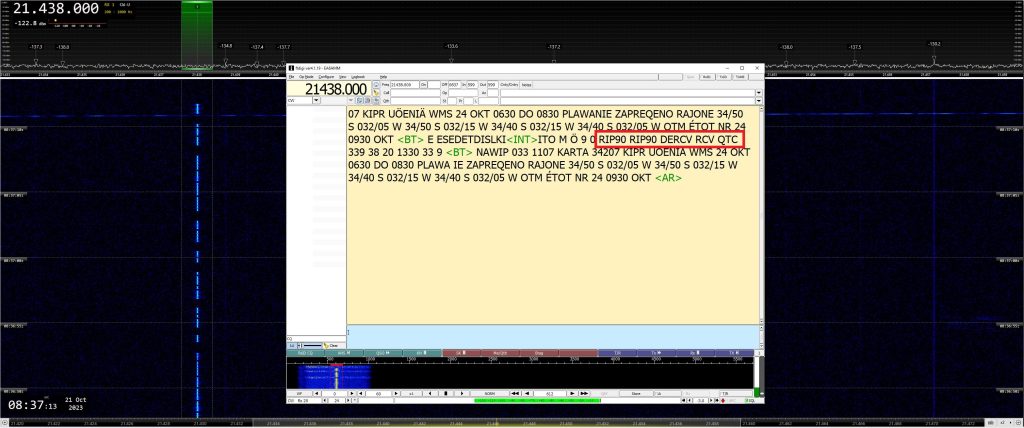
Below is an example of intrusion on the HF amateur bands using the CW — A1A transmission mode . It is the transmission of the “RCV” station, operated by the Russian Navy and located in the Sevastopol area, which transmits QTCs daily on 21.438 kHz
Radio-location of fishing buoys
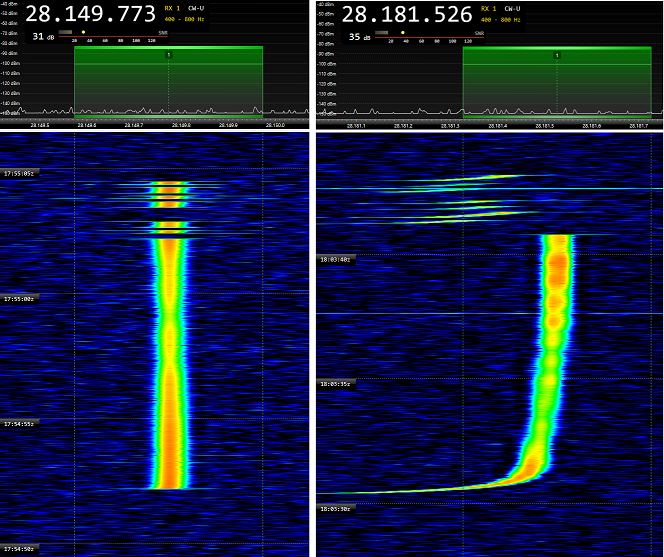
Within the CW A1A mode we also receive automatic transmissions sent by devices used for the radio-location of fishing buoys. These devices, integrated into fishing gear buoys, can have a range of more than 50 nautical miles (about 96 km).
They transmit in the 28 MHz band (10 meters). The transmission, repeated in variable periods of time, consists of the emission of a carrier lasting several seconds followed by a series of letters issued in Morse code. Often manufactured according to poor designs and /or using low-quality materials, many of them drift in frequency and transmit a poor quality signal.
CW — A1N
The ITU classification of emissions code A1N indicates:
A : Double side band.
1 : A single channel containing quantized or digital information, without the use of a subcarrier to modulate it.
N : No information transmitted.
It indicates a signal not transmitted in Morse code, such as random sequences of dots and dashes, continuous transmission of dashes or dots, etc.
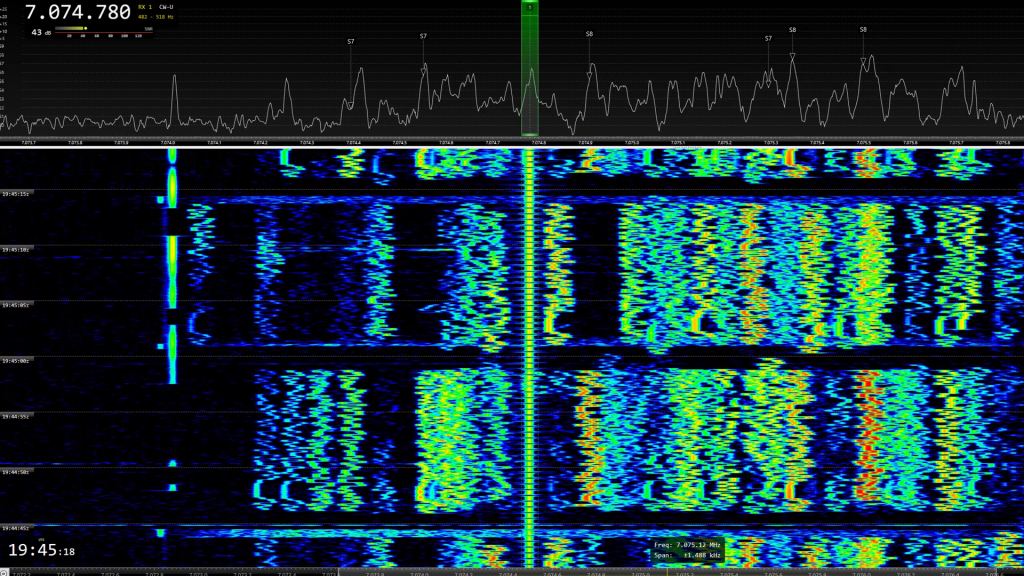
An example of this type of transmission that took place almost daily since 2021: 7075 kHz and very close frequencies, all of them included in the segment dedicated to FT‑8 mode in the 40 meter band. Transmission of groups of 16 dashes, or continuous dashes.